Wireless Network Monitoring
It has been a long while since wireless technology revolutionized businesses. Due to a large number of wireless devices servicing the world, the networks of this type keep growing. Some business processes cannot exist without wireless technology, such as moving objects management, warehouse logistics, net access in public places, hotel industry or sites where a wired network can hardly be set up.
Wireless technology has a lot of advantages adding more flexibility to business processes. The following advantages are among the basic ones:
- Mobility
- Configuration simplicity
- Low-cost deployment
- No wires
However, a wireless network has a series of imperfections:
- Frequent security threats
- Disruptions by interferences
- Lower general connection speed
- Slower speed with a large number of clients connected
Having your wireless network properly designed and configured doesn't help to avoid possible risks. The network status has to stay under regular monitoring, which includes the following subtasks:
- Wireless equipment monitoring
- Network availability and connection quality monitoring
- Client equipment monitoring (wireless terminals, mobile devices, etc.)
- Network access control
- Monitoring of services available in a wireless network
It's critical that the total network performance doesn't go down in this case. Moreover, a comprehensive approach allowing to see the status of the whole network is needed.
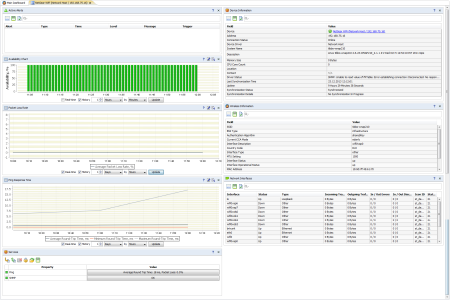
Solving these tasks is an easy job for AggreGate Network Manager which takes over the control of all your corporate wireless network components. The Manager keeps track of wireless network performance indicators, equipment, and provided services. AggreGate Network Manager contains a number of out-of-the-box wireless data visualization and mining tools. Here are only several metrics monitored by AggreGate Network Manager:
- General information on devices
- SSID wireless networks
- BSS type
- Authentication algorithm
- Addresses of connected, disconnected and unauthenticated clients
- Country code
- MTU setting
- Status and load, interface errors
- Memory state
- CPU load
- Device availability and response time