Configuration and Compliance Management
AggreGate Network Manager helps network administrators to track configurations of network devices and proactively react to diverse policy violations. The system backs up all configuration changes and offers a centralized compliance reporting.
Centralized Configuration Management
Every installation of the Network Manager in a large network has a huge database of connected devices, including routers, switches, wireless access points, firewalls, and more. This database is in most cases built using network discovery.
Configuration of all these devices can be periodically retrieved by the central server and backed up to the server database. In most cases, this requires no additional configuration, except for specifying devices' auth credentials.
System operators are immediately warned if a configuration change is detected by the periodic configuration polling or a change event was received from a device (e.g., in the form of a Syslog message or SNMP trap). This enables real-time network-wide monitoring of reconfiguration activities and quick isolation of incidents related to wrong configurations.
All historical configurations are stored in the central database until pre-configured expiration conditions force their deprecation. Those conditions, as well as backup schedules and network segments included in the backup process, can be customized by system administrators.
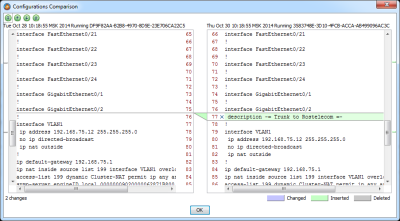
Administrators can browse the historical configuration database at any time and easily compare several configurations in a visual difference viewer. Several types of comparisons are supported:
- Comparison between historical versions of one configuration
- Comparison of different devices' configurations
- Comparison of several configuration types, e.g. startup to runtime
Any historical configuration can be re-uploaded to a device in a few mouse clicks. The baselining feature allows marking one, several or all device configurations as "known to work" and quickly revert to them in case of troubles.
Vendor-Agnostic Operations
Device configurations can be retrieved from a wide range of network hardware provided by different manufacturers. Even for a single hardware type, multiple configuration retrieval methods can be supported. For example, a Cisco device can be commanded via SSH, Telnet or SNMP, and the actual configuration read/write can rely on FTP, TFTP or SCP.
However, all configurations are kept in a generic multi-vendor storage allowing the unified approach to their comparison and validation.
Skilled AggreGate administrators can modify configuration read/write scripts adding support for new device makes, models or even types.
Change Management
AggreGate Network Manager can perform automatic reconfiguration of network devices by executing the so-called configuration scripts. Those scripts solve typical configuration change tasks, such as:
- Changing device's ACL
- Registering a new VLAN
- Shutting down or rebooting a device
- Modifying ARP table
- Enabling IP SLA or NetFlow
Configuration scripts are normally executed by the server through an SSH or Telnet session. Scripts are not static, they can refer to any server-side or device-side data to ensure that each device receives its own customized set of commands.
The scripting engine supports two different syntax variants for writing simple line-by-line scripts and implementing custom logic based on device replies.
All configuration scripts can be applied to multiple devices in a bulk mode at once. The execution can be started on-demand, scheduled or initiated by an alert.
Compliance Management
The Network Manager can test device configurations for compliance with federal regulations (such as PCI, HIPAA or SOX) or corporate security standards. All violations are immediately detected, and system operators get warned.
The compliance policies are rule-based. AggreGate Network Manager distribution includes a number of standard policies. However, existing policies can be fine-tuned, and new policies can be added on-demand.
Changed and newly created policies can be easily tested against any configuration. However, the normal system operation assumes that compliance is automatically checked each time a configuration change is detected. This makes the spot violation statistics available at any time, in addition to the scheduled reporting.
Typical configuration problems can be automatically remediated by launching a configuration script upon a Policy Violation alert.